LEARN YOUR NUMBERS AND FOLLOW THE FIVE ‘KEY’ STEPS TO OPTIMAL HEALTH
Biometric measurements help assess your health as well as indicate your risk for certain disease and medical conditions and often include blood pressure, body mass index, cholesterol, glucose and triglycerides. Knowing your numbers can empower you to reduce your risk for illness and disease, leading you on a path to optimum health and wellness.
A word about risk factors: Some risk factors can be modified, treated or controlled while others cannot. Risk factors that cannot be modified, treated or controlled include age, gender, family history, ethnicity and race. Risk factors that can be modified, treated or controlled include smoking, being overweight or obese, high blood cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, physical inactivity and diabetes.
Control Blood Pressure
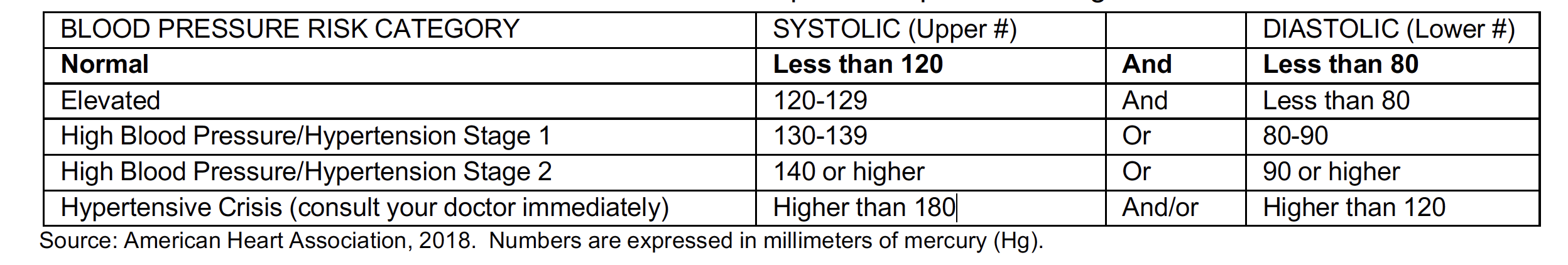
Blood Pressure is the force of blood pushing against artery walls as the heart pumps out blood. If this pressure rises and stays high, it can damage your heart, kidneys, eyes, and more.
- Reach and maintain a desirable body weight (see below).
- Follow the DASH Diet. Find DASH meal plan and guidelines at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/dash
- Limit sodium by eating more whole, unprocessed foods and using sodium free spices.
- Enjoy 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily. Check with your doctor before starting an exercise program.
- Limit alcohol
- Do not smoke
- Get adequate sleep
- Manage stress levels.
Reach and Maintain a Desirable Body Weight
Being overweight increases your chance of developing high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Promote gradual weight loss by eating less and burning more through physical activity. Visit www.myplate.gov to find out how many calories you need daily and the recommended number of servings from each food group.
- Too much fat in the stomach area increases disease risk. A waist measurement of more than 35 inches in women and more than 40 inches in men is considered high.
- Body Mass Index (BMI) a measure of body fat based on height and weight. It does not consider muscle to fat ratio, so if you work out and are increasing muscle mass, BMI may seem disproportionately high.

Source: National Institutes of Health (NIH). To calculate your BMI visit: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health//public/heart/obesity/lose_wt/BMI/bmicalc.htm
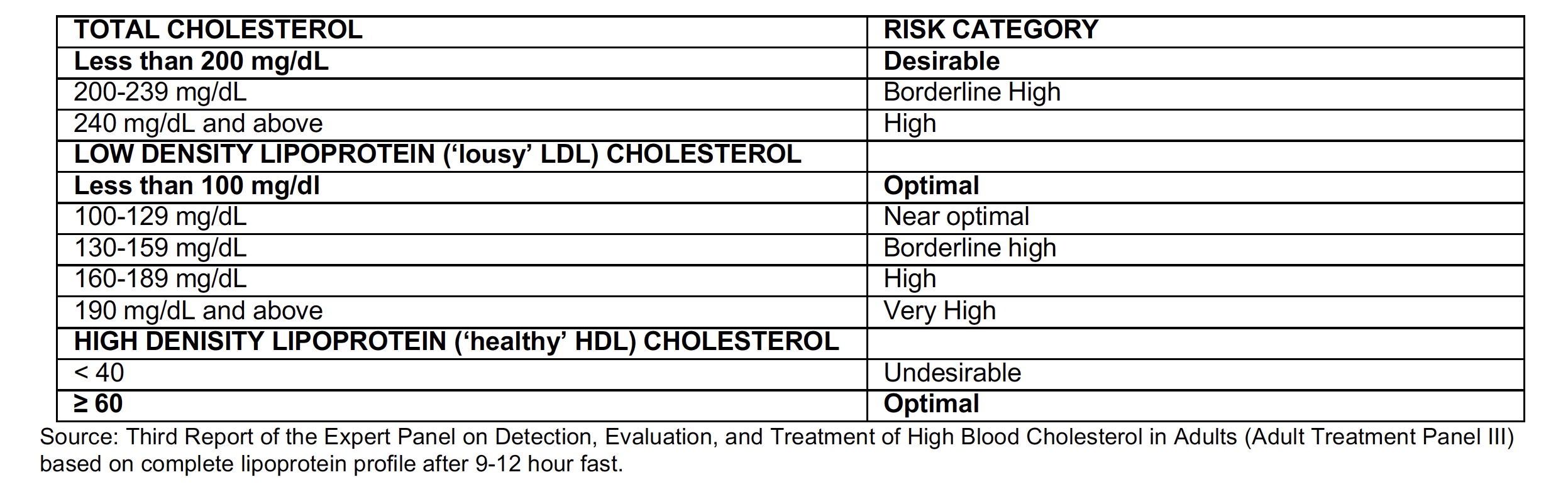
Control Blood Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a wax-like substance produced by the liver or eaten in certain animal foods. Too much cholesterol in the blood can cause arterial blockage and increases your risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Reach and maintain a desirable body weight (see above).
- Keep your intake of total fat to 25-35% of calories and focus on healthy unsaturated fat food sources.
- Limit saturated fat intake to less than 7% of calories and try to avoid all trans-fat.
- Consume plenty of fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Enjoy 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily. Check with your doctor before starting an exercise program.
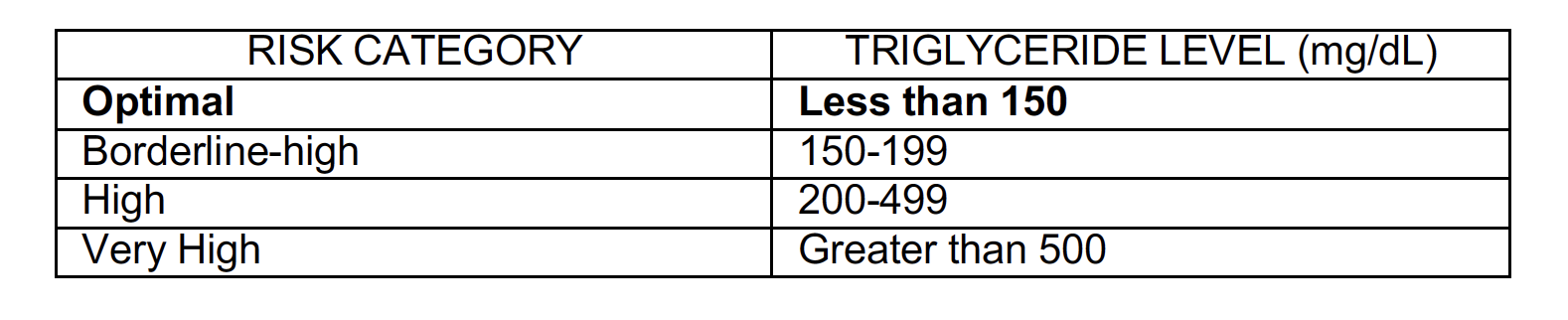
Control Triglycerides
Triglycerides are the chemical form in which fat exists in food as well as in the body. Elevated triglycerides can build up to unhealthy levels in the blood, raising the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Reach and maintain a desirable body weight (see above).
- Eliminate sugar and other refined carbohydrates foods and beverages.
- Limit saturated fat intake and try to avoid all trans-fat. Enjoy foods with unsaturated and omega-3 fats. Discuss omega-3 fatty acid supplementation with your physician and Registered Dietitian.
- Enjoy 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily. Check with your doctor before starting an exercise program.
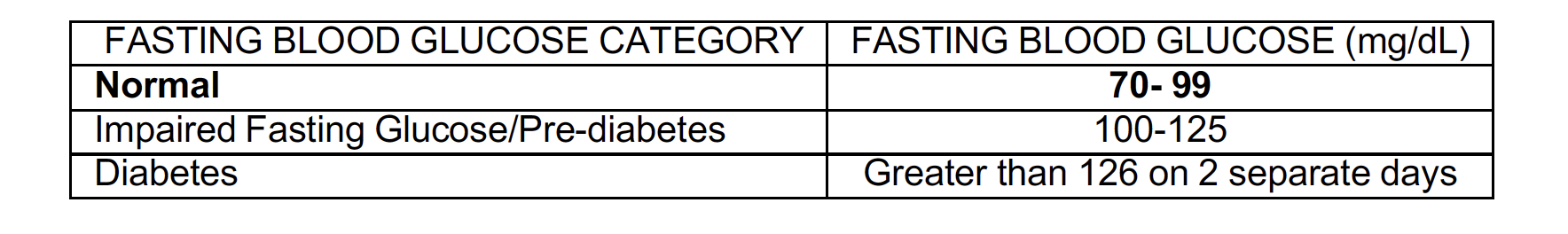
Control Blood Glucose
Glucose is measured in the blood to determine if a person has diabetes or pre-diabetes. Maintaining optimal blood glucose control minimizes your risk for developing many diseases.
- Reach and maintain a desirable body weight (see above).
- Eat a healthful diet including lean protein, whole grains, legumes, vegetables and fruits.
- Eliminate sugar and other refined carbohydrates foods and beverages.
- Limit saturated fat intake and try to avoid all trans-fat. Enjoy foods with unsaturated and omega-3 fats.
- Enjoy 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily. Check with your doctor before starting an exercise program.
- Work with a Registered Dietitian to help you develop a personalized meal plan: visit the website of the Academy of Nutrition & Dietetics, www.eatright.org and click on "Find a Registered Dietitian".